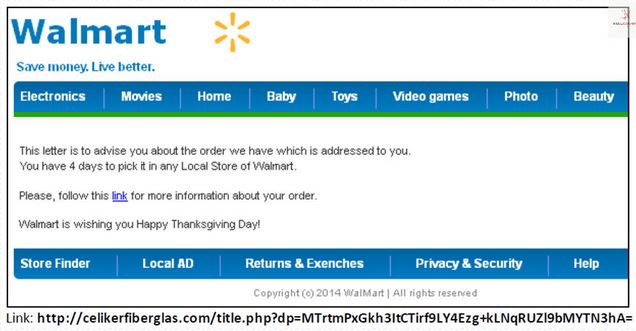
Is CHIP & PIN Credit Card Security Worth $100M? (Are You Serious?)
I’ve had dozens of media requests for interviews and countless more email inquiries from people concerned about the Target data breach. At first, everyone just wanted to know details of how it happened, how big the breach was, and what they should do about it if their credit cards were at risk. Now that the initial shock of it is over, we are on to a bigger question:
How do we keep breach from negatively affecting so many Americans?
Breach will always happen. If it’s digital, it’s hackable. It’s coming to light that the Target breach may have been due to the computer access an HVAC WORKER (no, not an entire company, an individual WORKER) had to Target’s systems. While there is no guaranteed way of preventing fraud, there is a pretty reliable answer out there, and it’s been around for decades. That answer is for the US to finally catch up to more than 80 countries around the world and start using chip and PIN enabled credit cards, also known as EMV, smart cards, or microchip cards.
By placing microchips in credit cards, it makes it much harder for criminals to clone the cards than the relatively easy-to-crack magnetic stripes. Chip cards take the cardholder information and turn it into a unique code for each transaction. They also often require additional authentication, such a personal identification number, or PIN. So in the case of the Target breach, the stolen data couldn’t be used to easily create duplicate credit cards, drastically reducing the value of the stolen data. The possibility for online abuse of the numbers (known as Card Not Present transactions) would remain a threat from the breach, but it would be a fraction of the problem (and solvable in other ways).
France has been using this technology since 1982, the UK since 2001, and Canada since 2007. In the first five years after the UK started using chip & PIN, fraud went down 70%. In that same time period, the cost for fraud in the US had DOUBLED. It’s not that the technology is perfect, it’s that the increased security convinces criminals to target those who don’t use the technology (which to this point has only been, well, the United States).
If there is such a great guarantee on fraud reduction by switching to chip and PIN cards, why is the US resisting it? The answer: MONEY. Banks, credit card companies, and retailers have been caught in a battle of wills for many years now, with retailers not wanting to spend money on installing new chip-friendly card readers unless banks are committed to spending money on issuing new cards.
The cost of implementing the card system can be staggering. Target is expected to spend around $100 million to install new chip card readers in an effort to protect against cyber theft.
So is it worth $100 million to implement chip and PIN technology?
Without question. And even Target thinks so, or at least it did ten years ago when it was at the forefront of implementing chip & PIN technology. From 2001-2004 they spent $40 million to adopt chip-based credit-card technology and installed 37,000 new point-of-sale terminals to handle chip cards across its U.S. stores.
Ultimately they backed out because their marketing strategy at the time just didn’t catch on with consumers and because it was taking “A FEW SECONDS” longer per customer to get through the line. I don’t know about you, but I’d wait an extra two seconds in order to know my data is secure. And I bet Target victims would take back the time it is taking them to change their credit card information with every online site or monthly automatic payment company their now-compromised card was used for.
To put the cost in perspective, $100 million is about $1.00 per Target breach customer. I bet the average credit card holder would be willing to foot the $1 bill to dramatically reduce their risk (even if it’s not a perfect solution). In fact, the cost of fraud gets passed on to customers anyway (higher credit card rates, higher retail prices), so why not spend that same money (or far less, in fact) on securing the transactions in the first place?
- A survey of 936 credit unions indicates the Target breach has cost credit unions an average of about $5.10 per card affected by the security lapse. The Credit Union National Association said these costs most likely do not include any fraud losses, which are likely to occur later.
- In 2012, the Ponemon Institute’s annual study showed the average cost of a data breach in the US is $188 per person notified.
- For credit issuers, the average cost per record breached is set at $280.
- Aite Group reports that card fraud in the U.S. already costs the card payment industry (primarily issuers) $8.6 billion a year.
You tell me if it’s worth it! (Seriously, I want your thoughts and comments below)
How do we get there?
It seems crystal clear to me that fraudsters have gotten so sophisticated that we either need to join together (retailers, banks, and credit card companies) or we will fail to stop this trend of Mega-Breaches. Pardon the pun, but clearly we have put the “target” on our own backs; criminals have increasingly focused on the US because we are so far behind.
James Dimon, CEO of J.P. Morgan Chase sees this as an opportunity for real change. He said, “All of us have a common interest in being protected, so this might be a chance for retailers and banks to for once work together, as opposed to sue each other like we’ve been doing the last decade.”
I see 4 overarching steps that need to be taken:
- Retailers, credit card processors, banks, VISA, MasterCard and American Express need to stop focusing on their own self-interest (profit) and start to work together for the common good. Of course, they won’t do this without incentive, so…
- Congress should create a U.S. equivalent of the U.K. Card Association that sets policy and has the authority to fine those stakeholders who fail to act.
- In other words, we will need legislation to ensure that the “liability shift” dates projected for 2015 are met. This means that if credit card companies have issued chip and PIN cards, but retailers have not installed machines to read them, the merchants would be held accountable for any losses due to fraud.
- Everyone needs to understand that there will be costs associated with the change, just like there are costs when you install a security system, a lock on a door or a vault in a bank.
Will chip and PIN cost retailers? Yes. Will chip and PIN cost banks? Yes. Will it cost consumers? Yes. Will it cost (in total) as much as the fraud resulting from even a single major breach like Target. NO. It’s time to start thinking about security from a long-term perspective, and long-term profitability will follow.
John Sileo is an author and highly engaging speaker on internet privacy, identity theft and technology security. He is CEO of The Sileo Group, which helps organizations to protect the privacy that drives their profitability. His recent engagements include presentations at The Pentagon, Visa, Homeland Security and Northrop Grumman as well as media appearances on Rachael Ray, 60 Minutes, Anderson Cooper and Fox Business. Contact him directly on 800.258.8076.

 Over the next ten years, wearable technology could change the way you live even more than smartphones have. Wearable technology combines all of the tracking, collecting and communicating power of current mobile devices with an intimate level of personal information captured in real-time. Common wearables include: Fitness Bands, GPS-enabled Cameras, Digital Glasses, Medical Devices and Smart Watches. Wearable technology can be a force for good, but you need to consider the privacy and security implications of the devices as well.
Over the next ten years, wearable technology could change the way you live even more than smartphones have. Wearable technology combines all of the tracking, collecting and communicating power of current mobile devices with an intimate level of personal information captured in real-time. Common wearables include: Fitness Bands, GPS-enabled Cameras, Digital Glasses, Medical Devices and Smart Watches. Wearable technology can be a force for good, but you need to consider the privacy and security implications of the devices as well. It will take at least 5 years for Chip and PIN (or EMV) transactions to make up the majority of retail card processing in the U.S.
It will take at least 5 years for Chip and PIN (or EMV) transactions to make up the majority of retail card processing in the U.S.